Traditional tiered link building no longer works. Creating backlinks to levels of linking pages to your website was once a way to improve site rankings through layered authority.
In the past, SEOs built links not just to their website but also to the pages that linked to them, referring to Tier 2 and Tier 3 links, in which the goal was to increase the power of Tier 1 backlinks and pass that strength down the chain.
How search engines like Google perceive and recognize backlinks today has evolved.
Contents
ToggleWhy Traditional Tiered Link Building Doesn’t Work?
While it’s a systematic approach to link building, traditional tiered link building no longer works for many reasons.
1. Link Decay and 404 Errors Break the Chain
Backlinks are not permanent, as the web is constantly changing. Pages get updated, deleted, or moved, particularly during this time when the rate of content publishing has accelerated. This means that your Tier 1 backlinks (the ones linking directly to your site) can eventually disappear. When that happens, the entire link chain breaks.
If you’ve invested time or money building Tier 2 links to boost a Tier 1 page, and that Tier 1 page goes offline (returns a 404 error or gets redirected), all the value from those Tier 2 links is lost. Google can’t crawl through a broken link to reach your site. As a result, the link equity stops flowing.
The challenge with this scenario is that it becomes worse over time. As websites restructure or remove content, the likelihood of link decay increases. Even high-authority sites can remove pages without notice. So, if your entire strategy depends on supporting a Tier 1 page that’s no longer active, you risk highly of your backlink profile.
2. Direct Links Pass More Value
In today’s SEO landscape, Google gives more weight to backlinks that point directly to your website, especially when those links come from authoritative, relevant sources.
When a site links to your page, Google views that link as a clear signal of trust, relevance, and endorsement. It’s direct, easy to crawl, and tied to content that users can immediately access. These links carry more ranking power and help improve your site’s visibility in a more predictable way.
Conversely, indirect links (those that are buried in a tiered structure (Tier 2 to Tier 1 to your site), lose their strength as they pass through multiple layers. Every jump from one page to another dilutes the potential link equity. If the Tier 1 page isn’t indexed, lacks authority, or is poorly optimized, even a strong Tier 2 link won’t help you. The benefit of layered link building stops before it reaches you.
A direct backlink embedded in meaningful content will outperform a tiered link structure built on low-value pages.
3. Contextual Relevance Matters More Than Structure
Google focuses heavily on contextual relevance. With hundreds of backlinks we build every single day with our link building agency, we’ve observed quite well how powerful relevant backlinks are to the website.
A backlink placed within content that matches your topics or industry will pass more value than one that’s technical “part of a tiered system.”
Google is better at understanding what content is about, so it expects backlinks to come from content that’s thematically aligned with the target page. For instance, if your site is about dental software, a link from a healthcare IT blog will be more valuable than one from a fitness receipt site (even if both pages technically point to your content).
Traditional tiered link building fails here because it often prioritizes link quantity over contextual quality. The end result is a chain of weak signals instead of a strong, relevant recommendation.
4. Harder to Track ROI and Value
When the strategy involves creating multiple layers of backlinks (Tier 2 to Tier 1 to your site), it becomes challenging to identify which links are actually making a difference.
Let’s say you build 10 tier 2 links to a blog post (Tier 1) that links to your site. Your rankings slightly improved, but where did the lift come from? Was it the Tier 1 link itself? Did one of the Tier 2 links influence it? Was it due to another backlink if Google found it elsewhere? There are no clear, direct signals to measure.
The more layers involved, the harder it is to isolate what’s working, making it extremely difficult to assess the return on investment on link building.
You need to know where your gains are coming from so you can focus on what works and eliminate what doesn’t. Tiered link-building strategies blur the bigger picture and create too many unknowns.
Link Stacking: Modern-Day Tiered Link Building (and Smarter Alternatives)
While traditional tiered link building is outdated, the core idea of strengthening your most valuable backlinks is essential for link development; we call it “link stacking”.
What is Link Stacking?
Link stacking is the strategic practice of amplifying the value of your strongest backlinks and replicating them more often by increasing their visibility, authority, and contextual relevance, without relying too much on artificial link structures.
Link Stacking Strategies That Work
Here are proven link-stacking strategies that work in 2025.
1. Identify and Replicate High-Impact Backlinks
The best way to start is to know which backlinks are worth amplifying and replicating. Run a backlink audit using link intelligence tools like Ahrefs, SEMRush, and MajesticSEO (see our hand-picked link building tools for SEO).
See backlinks from authority domains, driving real referral traffic and pointing to the most important pages (or your blog content, acquiring search traffic via ranking for informational queries).
Replicate these high-impact backlinks that have been driving significant value to your site (as doing more of them can help improve more of the metrics you’re looking at—referral traffic, rankings, brand visibility, etc.).
Study the content that earned the highest-impact links. Is it a how-to guide, a case study, a list of tools, a data-driven piece of content, or a citable element on a landing page?
Once you’ve identified the format and topic that attracted backlinks, create more content using the same structure and angle but more focused on new subtopics, updated trends, or related industry keywords.
For instance, if a list of “Top CRM Tools for 2025” earned strong backlinks, follow up with “Best CRM Tools for Startups”—these are pieces of content tailored to your target persona and aligned with the user’s buyer journey.
2. Do Smart Internal Linking
The authority on the page where you get the most links doesn’t have to stay confined to that page. You can use smart internal linking to direct some of that value to other important pages on your site.
Revisit your blog posts with the highest number of referring domains, resource pages with backlinks from authority sites, and landing pages that earned natural citations or mentions.
Add contextual internal links to the most important product/service pages, newer blog posts that need ranking support, and categories (or hub pages) that build topical depth.
You can add sections such as “related sources” at the bottom, embedded videos or downloadable tools, and internal navigation to deeper subtopics. Doing so increases the number of pages per visit, improves your site’s crawlability, and efficiently spreads SEO value across your content ecosystem.
3. Distribute Content Targeting Keyword Variations of Your Core Topic
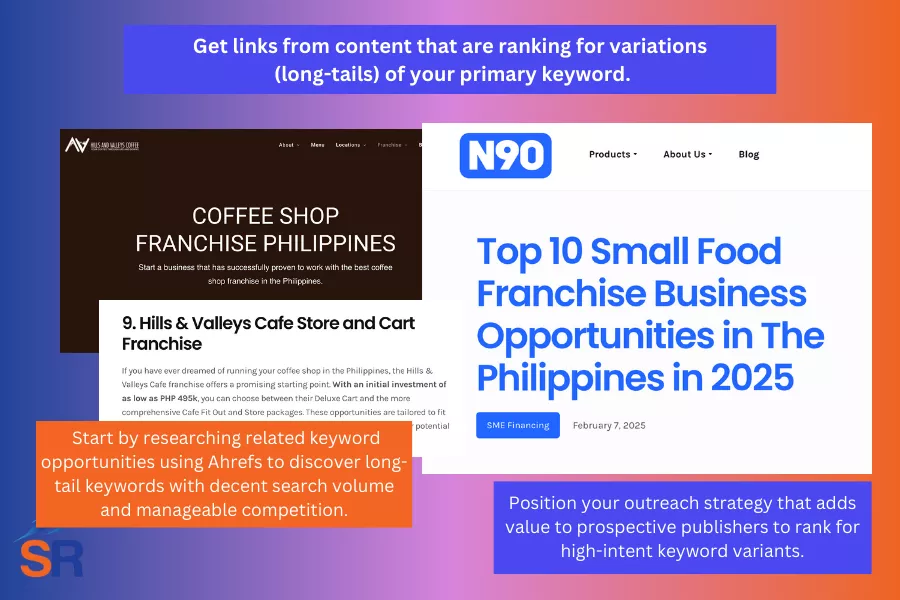
One way to scale your link stacking strategy is to create and distribute content that targets keyword variations related to your primary topics. Instead of repeating the same angle or keyword focus, this approach allows you to cover more ground and reinforce your site’s authority on a subject.
Google rewards topical depth, so as you consistently publish and earn links for content around a central theme, you start building your site’s topical authority (off-page).
Identify keyword variations with potential. Start by researching related keyword opportunities using Ahrefs or SEMRush to discover:
- Long-tail keywords tied to your core topic
- Variations with decent search volume and manageable competition
- Subtopics that address specific segments, pain points, or use cases
For instance, if your primary keyword is “project management tools,” variations might include “project management tools for remote teams” or “free tools for agile project workflows.”
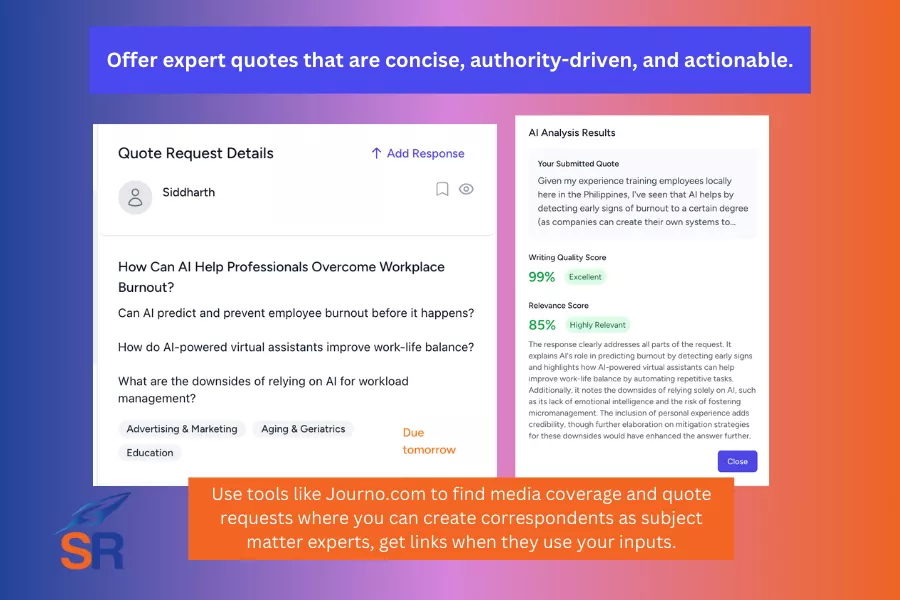
Do value-driven outreach.
Instead of simply soliciting backlinks, take a smarter route of offering to publish content on their site that targets keyword variations of your shared niche. The upside is that it’s geared towards the value it could bring to the table, benefiting your target publisher.
Mid-level publishers need more search traffic and quality content that ranks for new long-tail keywords optimized for underserved but high-potential queries.
You provide all that by offering content that targets specific keyword variations, ones with clear search intent and volume that may not be covered yet.
By positioning your outreach strategy that adds value to prospective publishers to rank for high-intent keyword variants, you increase the likelihood of higher responses and link placements that directly improve your site’s ability to rank for your primary keyword (as distributed content is topically relevant to what you’re trying to rank for).
4. Turn High-Performing Content Into Multi-Format Linkable Assets
When a piece of content earns strong backlinks, it clearly signals that it holds value for both users and publishers. You can multiply its link potential by turning it into various formats that attract different types of audiences, learners, and content creators.
Repurposing content pieces is a strategic link-stacking move to get more backlinks from more platforms using content that’s already proven to work.
A few formats you can consider:
- Infographics – visual summaries of stats or steps from your post
- PDF guide or downloadable – useful for resource pages or B2B listicles
- Slide decks – add more visual depth
- Short-form video – condense the content into explainer or how-to videos (which you can also upload to YouTube and earn organic social traffic).
By turning high-performing content into multi-format assets, you also increase the surface area of discovery through LLM’s AI models. The more accessible and multi-platform your content is, the higher the chance it gets referenced in AI-generated answers, included in citation stacks from AI tools, and more often suggested by Google’s AI Overviews.
Schedule a free strategy call if you’re looking for the best link building agency in the UK.
Written By
Venchito Tampon
CEO and Co-Founder at SharpRocket, a link building agency. With a decade of experience, Venchito has a proven track record of leading hundreds of successful SEO (link builidng) campaigns across competitive industries like finance, B2B, legal, and SaaS. His expert advice as a link building expert has been featured in renowned publications such as Semrush, Ahrefs, Huffington Post and Forbes. He is also an international SEO spoken and has delivered talks in SEO Zraz, Asia Pacific Affiliate Summit in Singapore, and Search Marketing Summit in Sydney, Australia. Check out his other business - Hills & Valleys Cafe.
Reviewed By

Sef Gojo Cruz
COO at SharpRocket, overseeing end-to-end operations, from crafting link building strategies to leading high-performing teams. Previously led SEO initiatives at Workhouse, a digital agency in Australia, and Keymedia, a real estate media company based in New Zealand.
How our LINK BUILDING AGENCY in UK builds 250 links/mo consistently using Predictable Link Building Methodology™…
- Using a SIMPLE and PROVEN system
- Using a SCALABLE strategy
- No private blog networks
- No creepy outreach emails